Liu, J., Satriadi, K. A., Ens, B., & Dwyer, T. (2024). Investigating the Effects of Physical Landmarks on Spatial Memory for Information Visualisation in Augmented Reality.
Investigating the Effects of Physical Landmarks on Spatial Memory for Information Visualisation in Augmented Reality
Jiazhou Liu, Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Barrett Ens, Tim Dwyer
IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR). Seattle, USA. 2024.
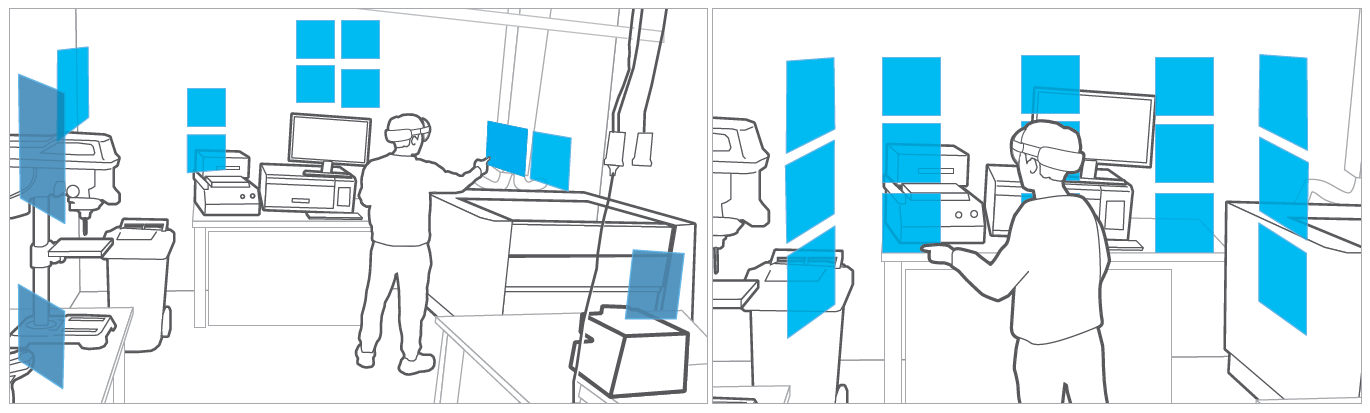
Augmented Reality (AR) is touted to be beneficial in supporting situated information display, allowing virtual information panels to be overlaid on real-world scenes. People must then use their spatial memory to navigate among these virtual panels effectively. While spatial memory has been studied in physical environments (wall displays) and virtual reality environments, there has been little research on how physical surroundings might affect memorisation of virtual content in a mixed environment like AR. Therefore, we provide the first AR study of spatial memory, comparing two different room settings with two different situated layouts of virtual targets on an abstract spatial memory task. We find that participants recall spatial patterns with greater accuracy and higher subjective ratings in a room with furniture compared to an empty room. Our findings lead to important design implications for mixed-reality user interfaces, particularly in information-rich applications like situated analytics and small-multiples information visualisation.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.29017.94563
Preprint: download
Presentation: watch
Tags: spatial memory, immersive analytics, view man-agement, physical landmark, cognition, augmented reality, mixed reality
Related Publications
-
Effects of Interface Layouts on Cognitive Performance for Pedicle Screw Placement Simulator in Immersive Environments
Lang Qin, Kadek Ananta Satriadi , Jiazhou Liu, Yuhan Zhan, Jiang Shao, Peimeng Liu, Zhiyong Chen, Yongtao Liu -
SADAS: A Dialogue Assistant System Towards Remediating Norm Violations in Bilingual Socio-Cultural Conversations
Yuncheng Hua, Zhuang Li, Linhao Luo, Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Tao Feng, Haolan Zhan, Lizhen Qu, Suraj Sharma, Ingrid Zukerman, Zhaleh Semnani-Azad, Gholamreza Haffari -
Context-Dependent Memory in Situated Visualization
Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Benjamin Tag, Tim Dwyer -
User-Driven Constraints for Layout Optimisation in Augmented Reality
Aziz Niyazov, Barrett Ens, Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Nicolas Mellado, Loïc Barthe, Tim Dwyer, Marcos Serrano -
Augmented Scale Models: Presenting Multivariate Data Around Physical Scale Models in Augmented Reality
Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Andrew Cunningham, Bruce H. Thomas, Adam Drogemuller, Antoine Odi, Niki Patel, Cathlyn Aston, Ross T. Smith -
Tangible Globes for Data Visualisation in Augmented Reality
Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Jim Smiley, Barrett Ens, Maxime Cordeil, Tobias Czauderna, Benjamin Lee, Ying Yang, Tim Dwyer, Bernhard Jenny -
Elicitation Study Investigating Hand and Foot Gesture Interaction for Immersive Maps in Augmented Reality
Christopher R. Austin, Barrett Ens, Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Bernhard Jenny -
Augmented Reality Map Navigation with Freehand Gestures
Kadek Ananta Satriadi, Barrett Ens, Maxime Cordeil, Tobias Czauderna, Wesley Willett, Bernhard Jenny